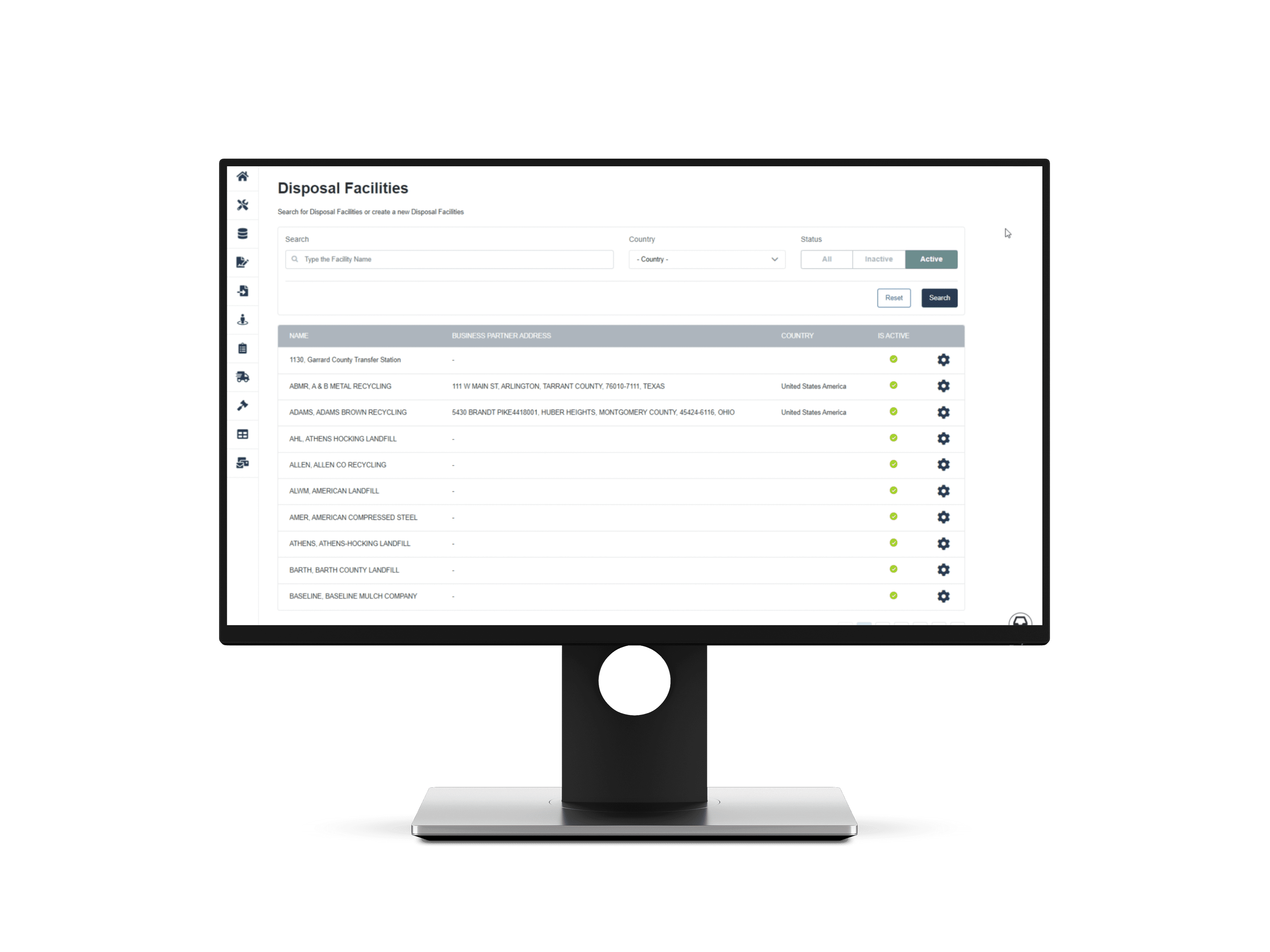
Software for Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a sustainable technology that converts organic waste into renewable energy. With a rich history dating back centuries, AD has gained significant traction in recent decades, driven by the need for sustainable solutions and government support. Advanced software tools are now essential for optimising AD plant operations, ensuring efficient production, and maximising financial returns.